In this article, we'll learn how to build a form using Next, TypeScript, and Formik. We'll be building a simple contact form with basic validation before submitting it. Formik is flexible library for building forms in React and React Native.
Set up project
Let's create the project for this tutorial. Open your terminal and enter the following command.
npx create-next-app@latest --ts nextjs-formik-demoThis will create a next project based on TypeScript. Here, I've named the project nextjs-formik-demo.
Once the project initialization is done, go to the project directory and run the development server.
cd nextjs-formik-demo
npm run devYour server will normally be running on localhost:3000.

Great, let's now modify the index.tsx file and create the form.
Creating the form
Before going further, let's install the bootstrap UI package. It'll be very useful to quickly create a form. We'll also install formik and yup.
npm install bootstrap formik yupOnce it's done go to index.tsx file and let's start modifying it.
First of all, let's import the packages we'll be using.
import { useState } from 'react';
import { useFormik } from 'formik';
import * as yup from 'yup';
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css';
...- useState: a hook that allows you to have state variables in functional components
- Formik: a React package that helps in forms creation, validation, and submission.
- Yup: a JavaScript schema builder for value parsing and validation
- bootstrap: we are directly importing the CSS files so we can use bootstrap CSS classes to style our components.
Next step, let's create values and object we'll be using for the next steps.
...
import type { NextPage } from 'next';
const Home: NextPage = () => {
const [message, setMessage] = useState(''); // This will be used to show a message if the submission is successful
const [submitted, setSubmitted] = useState(false);
const formik = useFormik({
initialValues: {
email: '',
name: '',
message: '',
},
onSubmit: () => {
setMessage('Form submitted');
setSubmitted(true);
},
validationSchema: yup.object({
name: yup.string().trim().required('Name is required'),
email: yup
.string()
.email('Must be a valid email')
.required('Email is required'),
message: yup.string().trim().required('Message is required'),
}),
});
...What are we doing here?
- message & submitted: This will help show a message that will be displayed when the form is successfully submitted
- formik: we use the
useFormikhooks to create a Formik object. It contains the initial values, theonSubmitmethod followed by a validation schemavalidationSchemabuilt withYup.
It's basically all we need for a form in just a few lines. Let's move to the UI and start using the formik object.
...
<div className="vh-100 d-flex flex-column justify-content-center align-items-center">
<div hidden={!submitted} className="alert alert-primary" role="alert">
{message}
</div>
<form className="w-50" onSubmit={formik.handleSubmit}>
{/* Adding the inputs */}
</form>
</div>
...We want to display an alert every time the form is successfully submitted. That's what this piece of code achieves:
<div hidden={!submitted} className="alert alert-primary" role="alert">
{message}
</div>We can now add the inputs. For each input, we'll be adding the label, the input and the error message for each field.
Let's start with the name field.
<form className="w-50" onSubmit={formik.handleSubmit}>
<div className="mb-3">
<label htmlFor="name" className="form-label">
Name
</label>
<input
type="text"
name="name"
className="form-control"
placeholder="John Doe"
value={formik.values.name}
onChange={formik.handleChange}
onBlur={formik.handleBlur}
/>
{formik.errors.name && (
<div className="text-danger">{formik.errors.name}</div>
)}
</div>
...
</form>And then the email field.
<form className="w-50" onSubmit={formik.handleSubmit}>
...
<div className="mb-3">
<label htmlFor="email" className="form-label">
Email
</label>
<input
type="email"
name="email"
className="form-control"
placeholder="john@example.com"
value={formik.values.email}
onChange={formik.handleChange}
onBlur={formik.handleBlur}
/>
{formik.errors.email && (
<div className="text-danger">{formik.errors.email}</div>
)}
</div>
...
</form>And next, the message field.
<form className="w-50" onSubmit={formik.handleSubmit}>
...
<div className="mb-3">
<label htmlFor="message" className="form-label">
Message
</label>
<textarea
name="message"
className="form-control"
placeholder="Your message ..."
value={formik.values.message}
onChange={formik.handleChange}
onBlur={formik.handleBlur}
/>
{formik.errors.message && (
<div className="text-danger">{formik.errors.message}</div>
)}
</div>
...
</form>And finally the submit button.
<form className="w-50" onSubmit={formik.handleSubmit}>
...
<button type="submit" className="btn btn-primary">
Send
</button>
</form>And here's the final code of the form.
<div className="vh-100 d-flex flex-column justify-content-center align-items-center">
<div hidden={!submitted} className="alert alert-primary" role="alert">
{message}
</div>
<form className="w-50" onSubmit={formik.handleSubmit}>
<div className="mb-3">
<label htmlFor="name" className="form-label">
Name
</label>
<input
type="text"
name="name"
className="form-control"
placeholder="John Doe"
value={formik.values.name}
onChange={formik.handleChange}
onBlur={formik.handleBlur}
/>
{formik.errors.name && (
<div className="text-danger">{formik.errors.name}</div>
)}
</div>
<div className="mb-3">
<label htmlFor="email" className="form-label">
Email
</label>
<input
type="email"
name="email"
className="form-control"
placeholder="john@example.com"
value={formik.values.email}
onChange={formik.handleChange}
onBlur={formik.handleBlur}
/>
{formik.errors.email && (
<div className="text-danger">{formik.errors.email}</div>
)}
</div>
<div className="mb-3">
<label htmlFor="message" className="form-label">
Message
</label>
<textarea
name="message"
className="form-control"
placeholder="Your message ..."
value={formik.values.message}
onChange={formik.handleChange}
onBlur={formik.handleBlur}
/>
{formik.errors.message && (
<div className="text-danger">{formik.errors.message}</div>
)}
</div>
<button type="submit" className="btn btn-primary">
Send
</button>
</form>
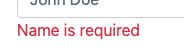
</div>And the form is operational now. If you noticed, we are conditionally showing errors in the forms using formik.errors.
{formik.errors.name && (
<div className="text-danger">{formik.errors.name}</div>
)}This will display an error under the name field for example.
Here's the final code for index.tsx.
import { useState } from 'react';
import { useFormik } from 'formik';
import type { NextPage } from 'next';
import * as yup from 'yup';
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css';
const Home: NextPage = () => {
const [message, setMessage] = useState(''); // This will be used to show a message if the submission is successful
const [submitted, setSubmitted] = useState(false);
const formik = useFormik({
initialValues: {
email: '',
name: '',
message: '',
},
onSubmit: () => {
setMessage('Form submitted');
setSubmitted(true);
},
validationSchema: yup.object({
name: yup.string().trim().required('Name is required'),
email: yup
.string()
.email('Must be a valid email')
.required('Email is required'),
message: yup.string().trim().required('Message is required'),
}),
});
return (
<div className="vh-100 d-flex flex-column justify-content-center align-items-center">
<div hidden={!submitted} className="alert alert-primary" role="alert">
{message}
</div>
<form className="w-50" onSubmit={formik.handleSubmit}>
<div className="mb-3">
<label htmlFor="name" className="form-label">
Name
</label>
<input
type="text"
name="name"
className="form-control"
placeholder="John Doe"
value={formik.values.name}
onChange={formik.handleChange}
onBlur={formik.handleBlur}
/>
{formik.errors.name && (
<div className="text-danger">{formik.errors.name}</div>
)}
</div>
<div className="mb-3">
<label htmlFor="email" className="form-label">
Email
</label>
<input
type="email"
name="email"
className="form-control"
placeholder="john@example.com"
value={formik.values.email}
onChange={formik.handleChange}
onBlur={formik.handleBlur}
/>
{formik.errors.email && (
<div className="text-danger">{formik.errors.email}</div>
)}
</div>
<div className="mb-3">
<label htmlFor="message" className="form-label">
Message
</label>
<textarea
name="message"
className="form-control"
placeholder="Your message ..."
value={formik.values.message}
onChange={formik.handleChange}
onBlur={formik.handleBlur}
/>
{formik.errors.message && (
<div className="text-danger">{formik.errors.message}</div>
)}
</div>
<button type="submit" className="btn btn-primary">
Send
</button>
</form>
</div>
);
};
export default Home;And voilà. We've just integrated Formik to a Next project in Typescript with Boostrap and Yup.
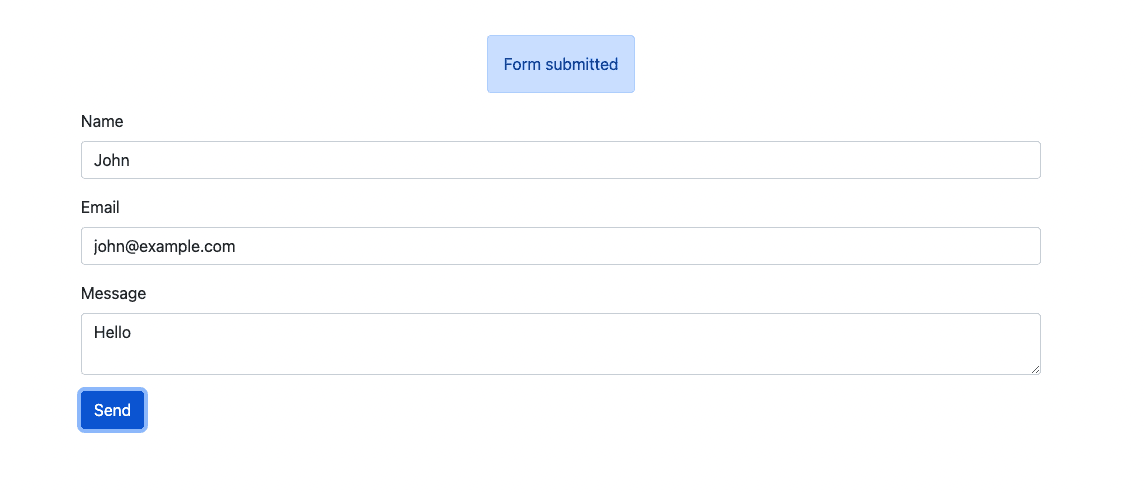
Here's a GIF showing the demo.
Conclusion
In this article, we've learned how to build a contact form using Formik and Yup with Next and TypeScript.
Building a simple form with Formik and Next.js is definitively overkill, my story about React SaaS Boilerplate is a showcase on to build complex SaaS application. You'll find on how to implement advanced features like user authentication and dashboard where forms need to be integrated with a backend REST API.
As an alternative to Formik library, I have written another article about React hook form Nextjs. A modern way to build form in React with Hooks with an easier and cleaner code.
